FTPS
File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS) is an extension of the standard FTP protocol that adds support for Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) cryptographic protocols. FTP(S) is widely used for secure business-to-business file exchanges, providing encryption for both authentication credentials and data transfers. Unlike SFTP, which operates over SSH, FTP(S) extends the traditional FTP protocol by layering security on top of the standard FTP command set.
FTP(S) supports three encryption modes:
- Explicit FTPS (FTPES)
- Implicit FTPS
- None (Standard FTP)
The FTP(S) process involves several key steps:
- Connection Initiation: The client initiates a TCP connection to the server (usually on port
21for control, with additional ports for data transfer). - TLS/SSL Negotiation: The client and server negotiate encryption algorithms and establish a secure connection (either implicit or explicit Encryption Mode).
- Certificate Exchange: The server presents its SSL/TLS certificate, which the client verifies against trusted certificate authorities.
- Authentication: The client authenticates using a username and password over the encrypted control channel.
- FTP(S) Transfers: A separate encrypted channel is established for file transfers, securing both commands and data. The client begins file operations.
UDMG FTP(S) Implementation
UDMG's role in FTP(S) communications is determined by the Endpoint types used in your Pipeline configuration. UDMG can act as the FTP(S) Server or the FTP(S) Client. This flexibility allows UDMG to integrate with various partner scenarios: whether your partner exchanges files with you (UDMG as server) using their FTPS client, or you need to exchange files with them (partner's external FTP(S) server), using UDMG as the client.
This allows UDMG to interoperate with partners regardless of whether they must send or receive files, while supporting both unencrypted FTP and Explicit FTPS (FTPES).
UDMG as FTP(S) Server
This configuration involves a UDMG as FTP(S) Server Pipeline.
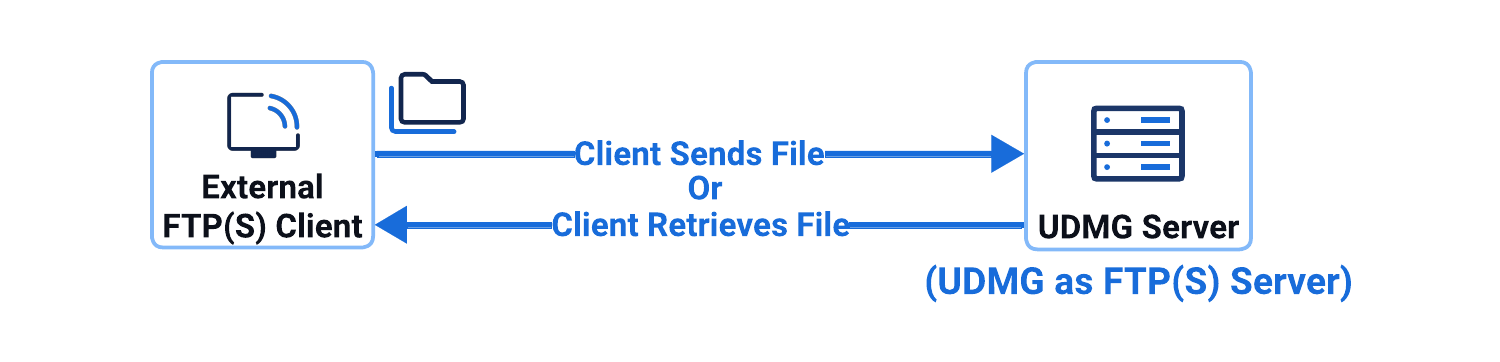
In this configuration:
- UDMG hosts and operates the Local FTP Server Endpoint.
- External partners connect to UDMG using an FTP or FTPS client.
- Partners manage files and folders.
- Files are saved to a filesystem (defined in the Local Filesystem Endpoint).
UDMG as FTP(S) Client
- Push Scenario
- Pull Scenario
This configuration scenario involves a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Push Scenario) Pipeline, where UDMG sends files from the local filesystem to an external FTP(S) server.
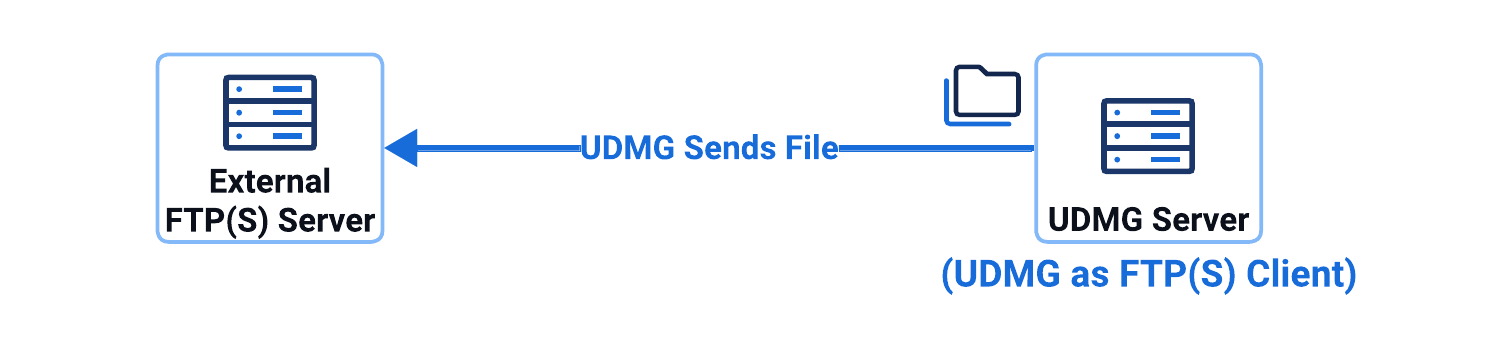
In this configuration scenario:
- UDMG has access to a filesystem (defined in a Local Filesystem Endpoint).
- UDMG sends the file to your partner's server, defined in the Remote FTPS Server Endpoint.
This configuration scenario involves a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, where UDMG retrieves files from an external FTP(S) server into the local filesystem.

In this configuration scenario:
- UDMG connects to an external FTP(S) server (defined in a Remote FTPS Server Endpoint) as a client.
- UDMG downloads (pulls) files from the external FTP(S) and saves them to a filesystem (defined in a Local Filesystem Endpoint).
FTPS (Explicit TLS) may be used to encrypt both control and data channels.