SFTP Protocol
The SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a secure network protocol used to transfer files over an encrypted SSH connection. It is widely adopted for business-to-business file exchanges due to its strong encryption, reliability, and support for automation. Unlike FTP or FTPS, SFTP runs within the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol and uses a single encrypted channel for both commands and data.
The SFTP process involves several key steps:
- Connection Initiation: The client initiates a TCP connection to the server.
- SSH Handshake: Both parties negotiate encryption, compression, and message integrity algorithms.
- Host Key Verification: The server presents its host key, which the client verifies against known keys.
- Authentication: The client authenticates using a password, public key, or both, depending on server configuration.
- SFTP Transfers: Once authenticated, the client begins file operations using the SFTP protocol.
UDMG SFTP Implementation
UDMG's role in SFTP communications is determined by the Endpoint types used in your Pipeline configuration. UDMG can act as the SFTP Server or the SFTP Client. This flexibility allows UDMG to integrate with various partner scenarios: whether your partner exchanges files with you (UDMG as server) using their SFTP client, or you need to exchange files with them (partner's external SFTP server), using UDMG as the client.
UDMG as SFTP Server
This configuration involves a UDMG as SFTP Server Pipeline.
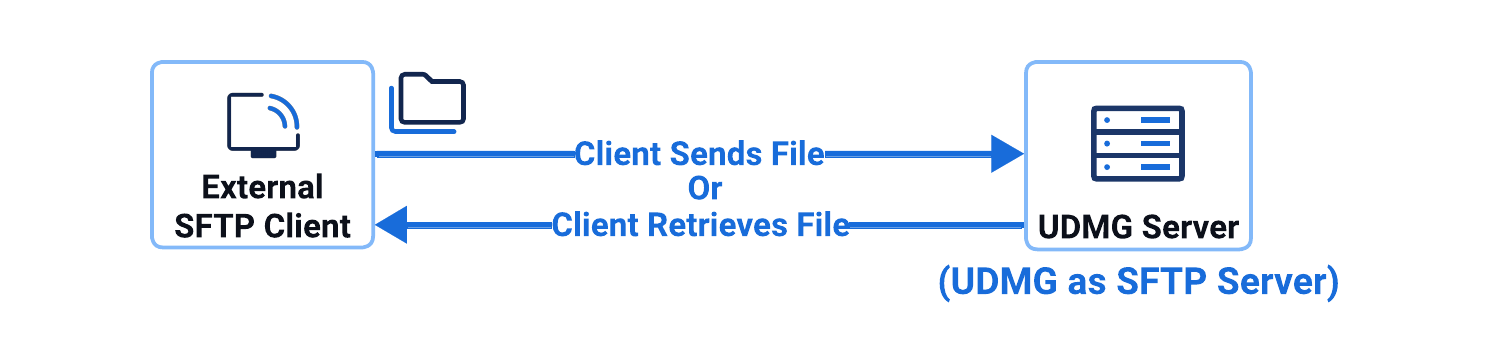
In this configuration:
- UDMG hosts and operates the SFTP Server Endpoint locally.
- External clients connect to UDMG's Local SFTP Server Endpoint.
- UDMG receives files from remote clients, or
- Client retrieves (pulls) files from UDMG.
UDMG as SFTP Client
- Push Scenario
- Pull Scenario
This configuration scenario involves a UDMG as SFTP Client (Push Scenario) Pipeline, where UDMG sends files from local filesystem to external SFTP server.
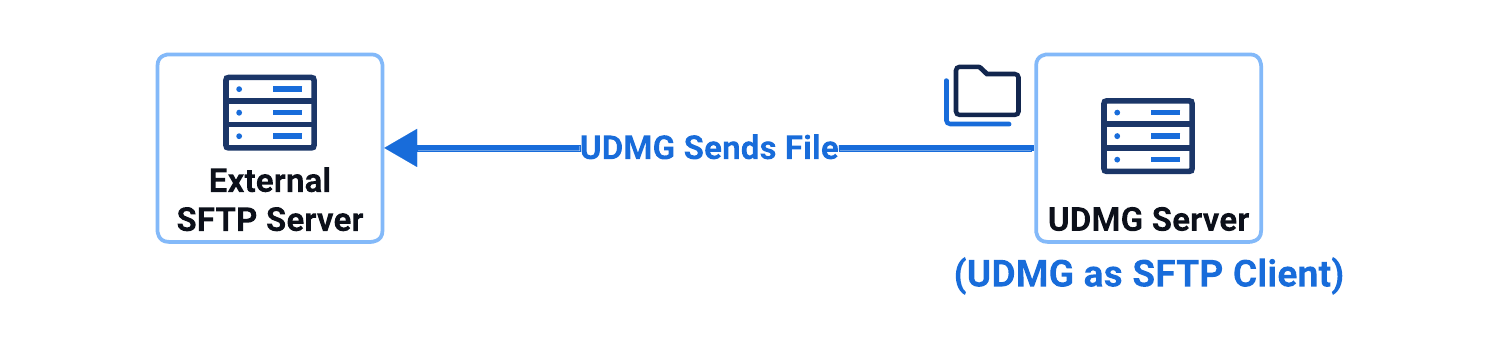
In this configuration scenario:
- UDMG's Remote SFTP Server Endpoint connects to an external SFTP server as a client.
- UDMG can pushes files to an external SFTP server.
This configuration scenario involves a UDMG as SFTP Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, UDMG retrieves files from external SFTP server to local filesystem.

In this configuration scenario:
- UDMG's Remote SFTP Server Endpoint connects to an external SFTP server as a client.
- UDMG can pull files from an external SFTP server.
Supported Versions
UDMG supports SFTP protocol version 3 in both:
- Server mode: Local SFTP Server Endpoints
- Client mode: Remote SFTP Server Endpoints
Supported Host Keys
The Host Key of a Local SFTP Server Endpoint must be a Private Key, and the Host Key of a Remote SFTP Server Endpoint must be a Public Key. Any of the following key types are allowed:
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
- ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
The host private keys must be entered in one of the following formats:
- PKCS#1 PEM-encoded
Keys start with
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- - PKCS#8 PEM-encoded
Keys start with
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- - OpenSSH
Keys start with
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
The host public keys must be entered in OpenSSH public key format RFC 4253.
Supported Algorithms
All of the following algorithms except diffie-hellman-group14-sha256 and curve25519-sha256@libssh.org are selected by default for SFTP Endpoints (Local SFTP Servers and Remote SFTP Servers).
| Type | Ciphers/Protocols | Restrictions / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Host Key |
| DSA keys only accept 1024 bytes, and the key must be in PEM PKCS1 format (between BEGIN DSA and END DSA lines) |
| Key Exchange (KEX) |
Disabled by default:
|
|
| Ciphers |
| |
| Message Authentication Codes (MACs) |
|