UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario)
The UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline enables UDMG to act as an FTP(S) client, pulling files from the external FTP(S) server to the local UDMG filesystem.
This Pipeline consists of:
- A Remote FTP(S) Server Endpoint that represents your partner's FTP(S) server (used as the Source Endpoint).
- A Local Filesystem Endpoint that represents the location of the files to be transferred (used as the Destination Endpoint).
- Pipeline-specific configuration options.
- An HTTP request to the Transfer Scheduled API.
Before You Begin
Prerequisites
Before configuring this Pipeline, we recommend you first:
- Obtain your partner's FTP(S) server connection details from their administrator, including hostname, port, and authentication credentials.
- Identify your local source directory and ensure that UDMG has the necessary permissions to read files from it.
- Test network connectivity to your partner's FTP(S) Server and manually verify that authentication succeeds.
- Prepare API integration setup and have a UDMG User with domain-level permissions.
Understanding Paths in FTP(S) Client Pipelines (Pull Scenario)
When configuring a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, several path fields determine where files are read from locally and where they are written to on the external FTP(S) server.
Each path has a specific role and is combined during runtime to build the complete source and destination paths used in transfers.
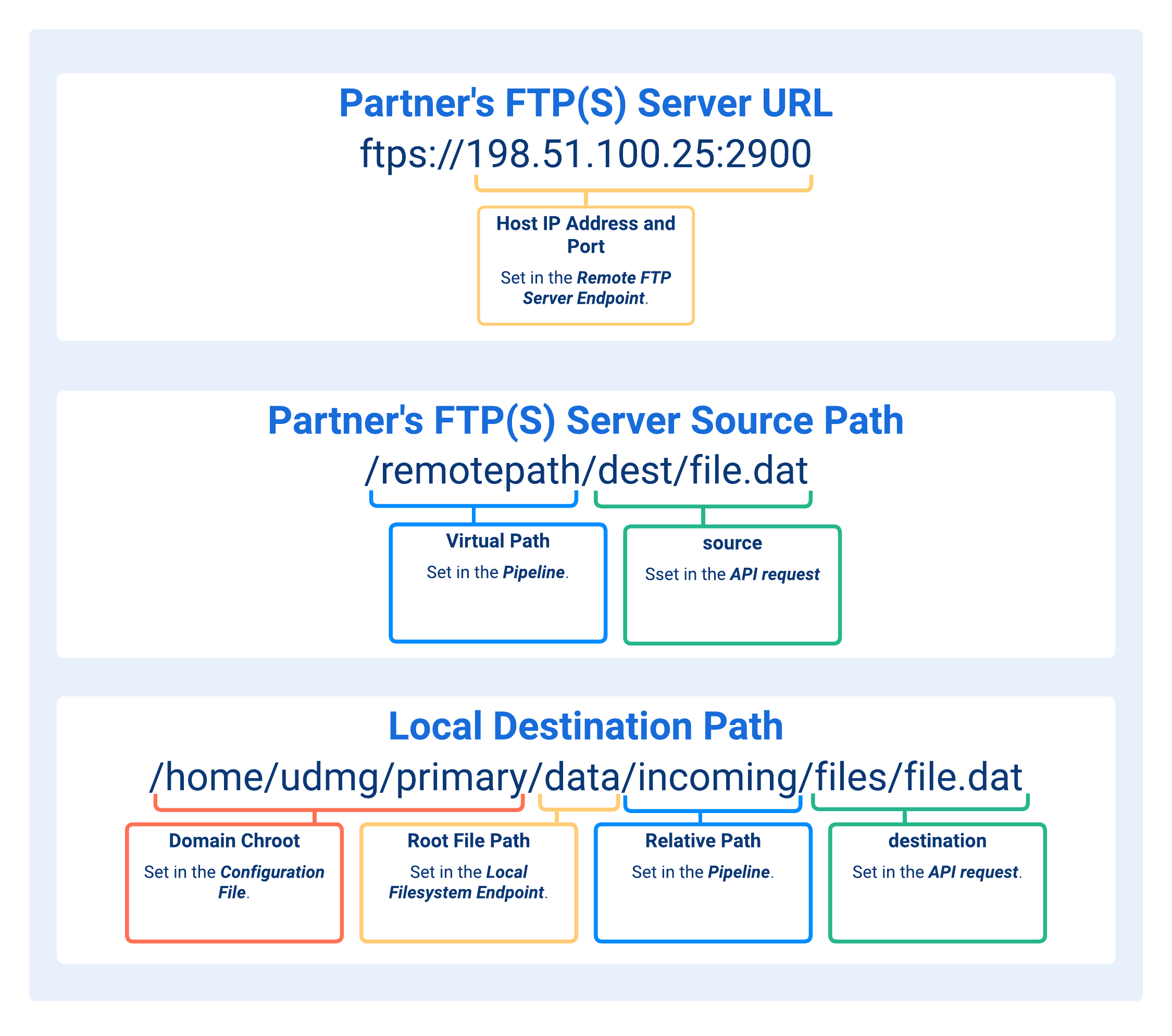
- Host IP Address and Port
- Virtual Path
- source
- Domain Chroot
- Root File Path
- Relative Path
- destination
The IP Address and Port of your partner's FTP(S) Server.
They are defined in the Remote FTP(S) Server Endpoint used as the Source Endpoint for this Pipeline.
The path where the file to be transferred exists on the partner's FTP(S) Server (not managed by UDMG).
Valid formats:
//[path]/[path]/[subdir]
The path must exist on your partner's FTP(S) Server.
Mandatory filename and extension of the file to be pulled. Optionally, it can include one or more subdirectories within the defined Virtual Path.
Valid formats:
/[filename.ext]/[path]/[filename.ext]/[path]/[subdir]/[filename.ext]
For implementation details, see Transfer Initialization via Scheduled API.
Depends on the domain_chroot argument defined in the Configuration File, which specifies the base path UDMG prepends at runtime. Valid argument values are:
NONE: No path is added.WORKDIR: The file path is resolved relative to thework_directory_pathargument defined in the Configuration File.WORKDIR+DOMAIN: Same asWORKDIR, but UDMG also prepends the Domain name. For example, if thework_directory_pathis/home/udmg/and the Domain name isprimary, the resulting path portion is/home/udmg/primary.
- Default value for
domain_chrootisWORKDIR+DOMAIN. - Default value for
work_directory_pathis/home/udmg/.
Path that establishes the storage hierarchy for all transferred files and provides the critical reference point for enforcing permissions across the file system structure.
It is defined in the Local Filesystem Endpoint used as the Destination Endpoint for this Pipeline.
The Relative Path completes the directory where files are written.
Valid formats:
//[path]/[path]/[subdir]/
It is defined in this Pipeline configuration.
It completes the full path of the destination file to be written. It must include the filename and extension, and may also include one or more subdirectories within the Relative Path provided in Destination Endpoint. It is typically provided as a parameter in the API request when triggering a transfer.
Valid formats:
/[filename.ext]/[path]/[filename.ext]/[path]/[subdir]/[filename.ext]
For implementation details, see Transfer Initialization via Scheduled API.
External FTP(S) Server Authentication
Pipelines where UDMG acts as a client—more specifically, those that contain a Remote FTP(S) Server Endpoint—require credentials to authenticate with the external FTP(S) server.
Unlike Pipelines, where UDMG acts as the server and relies on Accounts to supply credentials, these Pipelines define credentials directly within the Pipeline configuration.
This design enables each Pipeline to manage its own client authentication credentials independently. As a result, each Pipeline can only authenticate with one external system and use one distinct Credential Type at a time.
Supported Authentication Methods
UDMG supports three authentication methods when connecting to external FTP(S) servers. The external FTP(S) server configuration determines the required authentication method and must be provided by the server administrator.
Each Pipeline can only have one Credential Type associated with it at one time.
Transfer Initialization via Scheduled API
The Pipeline must be explicitly scheduled and triggered through the Transfers Scheduled API, using the configuration provided at the Pipeline level and API. You must first create the Pipeline using the Field Descriptions below, providing Endpoint-specific information. From there, to initiate a Transfer, you must submit an API request using the API Endpoint with the Pipeline name, the location and name of the file on the external FTP(S) server to be transferred, and the execution timestamp. Optionally, you can provide a specific destination path for where the file is to be transferred on UDMG. Transfers can be executed in real-time or scheduled for a specific future time.
This design enables precise control over file movement and allows each Transfer to be dynamically customized and scheduled.
API Endpoint
Path
POST /api/v1/domains/${UDMG_DOMAIN_NAME}/transfers
Request Body
The request body includes the following fields:
| Key | Description | Format | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
pipeline | Name of the Pipeline. | Exact match to the Pipeline's Name field. | Yes |
when | Date and time for executing the file transfer. If a date in the past is provided, the Transfer is initiated after the next system pending transfer check (transfer.checkInterval parameter is defaulted to every minute). | Must be in RFC3339 format ("2025-01-01T00:00:00Z"). | Yes |
source | The exact path where the file to be transferred exists on the external FTP(S) server. The parameter is appended to the Pipeline's Virtual Path to create a full path. The full path is Virtual Path + destination parameter. | Format: /[subdir]/[filename.ext] or /[file name.txt] | Yes |
destination | The path where the file is to be transferred to on UDMG locally. The parameter is appended to the Pipeline's associated Root Path and Relative Path to create a full path. The full path is work_directory_path + Root Path + Relative Path + destination parameter. If the file needs to be added to a subdirectory, then it should be added to the parameter. The file name needs to be changed, then it should be changed with the parameter. If the field is left blank, then it is transferred to the work_directory_path + Root Path + Relative Path. | Format: /[subdir]/[filename.ext] or /[same or new file name.txt] | No |
Example: Full Configuration and Path
| UDMG Global | Source Endpoint Path 1 | Source Endpoint Path 2 | Pipeline Path 1 | Pipeline Path 2 | Pipeline Scheduler API Parameter 1 | Pipeline Scheduler API Parameter 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| API Parameter | workingDirectoryPath | path | tmp | relative | virtual | source | destination |
| GUI Field | - | Root Path | Temporary Path | Relative Path | Virtual Path | - | - |
| Example | home/udmg | /receivedfiles | - | /newfiles | /ABC | /DEF/test.txt | /latest/ |
- Resulting Source Path (full):
/ABC/DEF/test.txt - Resulting Destination Path (full):
/home/udmg/receivedfiles/newfiles/latest/test.txt
Scheduling a File Transfer via API
Use the following curl command to schedule a file transfer through the Transfers Scheduled API:
curl http://<UDMG_HOST>/api/v1/domains/${UDMG_DOMAIN_NAME}/transfers \
-X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"pipeline": "SupplierA_Pipeline2",
"when": "2025-07-03T15:43:52.344Z",
"source": "/DEF/test.txt",
"destination": "/latest/"
}'
Retrieving Scheduled Transfers
Use the following curl command to view the list of scheduled transfers.
curl http://<UDMG_HOST>/api/v1/domains/${UDMG_DOMAIN_NAME}/transfers/scheduled
-X GET \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
{
"id": 1,
"pipeline": "SupplierA_Pipeline2",
"username": "robi",
"source": "/ABC/DEF/test.txt",
"destination": "/receivedfiles/newfiles/latest/test.txt",
"schedule": "2025-07-03T15:43:52.344Z",
"status": "Completed",
"executedAt": "2025-08-22T20:44:02Z",
"completedAt": "2025-08-22T20:44:02Z"
}
Adding a Pipeline
To add a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, follow these steps:
- From the Sidebar, select Configuration > Pipelines.
- Click Add Pipeline.
- Complete the Name for the new Pipeline.
- Select the Source Endpoint with a Remote FTP(S) Server Endpoint type.
- Select the Destination Endpoint with a Local Filesystem Endpoint type.
- Fill out the dynamic fields following the Field Descriptions table.
- Click Add.
UDMG does not allow for the creation of identical Pipelines (even with unique names). The Pipeline must pass the Source Endpoint + Destination Endpoint + Permissions + Virtual Path uniqueness check. See Pipelines for more information on Pipeline validation checks.
Field Descriptions
| Name | Description | Specifications | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Pipeline. |
| Yes |
| Description | Description for the Pipeline. | No | |
| Source Endpoint | The Source Endpoint is where files are retrieved, originated, or come from. Select Remote FTP(S) Server from the dropdown menu. |
| Yes |
| Destination Endpoint | The Destination Endpoint is where files are delivered to or sent. Select Local Filesystem from the dropdown menu. |
| Yes |
| Relative Path | The path where the file is to be transferred to on UDMG locally. The path is used to create a full path. The full path is work_directory_path + Root Path + Relative Path + destination parameter. | Format: /, /[path], or /[path]/[subdir]. The subdirectory and file name should not be included here if they are added within the destination parameter. | Yes |
| Virtual Path | The exact path or 'Remote Server Path' where the file to be transferred exists on the external FTP(S) server. The Transfers Scheduled API | Format: /, /[path], or /[path]/[subdir]. The subdirectory and file name should not be included here if they are added within the source parameter. | Yes |
| Credentials Name | The client authentication Credentials used to authenticate to the external FTP(S) server. | Must reference an already created Credential of type Username and Password, Username and Key, or Username, Password, and Key. | Yes |
| Universal Event | While this field is currently in the form, it's not used in the remote transfer configuration. | No |
Editing a Pipeline
To edit a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, follow these steps:
- From the Sidebar, select Configuration > Pipelines.
- Click the Name of the Pipeline you want to edit.
- Click the Edit button above the Pipeline details.
- Edit details for the Pipeline.
- The Source Endpoint and Destination Endpoint cannot be changed after creation.
- Click Update.
Upon Pipeline update, UDMG checks for Endpoint Source + Endpoint Destination + Configuration + Virtual Path uniqueness.
Managing a Pipeline
All Pipelines support the ability to view the complete Pipeline and linked Endpoint details.
Viewing Pipeline Details
To view the details of a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, follow these steps:
- From the Sidebar, select Configuration > Pipelines.
- Click the Name of the Pipeline you want to view.
- Click the Overview Tab or Details Tab to see additional Pipeline and Endpoint details.
Pipeline Metadata
Pipeline details include all parameters given in the Field Descriptions table, plus the following read-only metadata:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| UUID | Universally Unique Identifier of this Pipeline. |
| Version | Version number of the configuration. Every change increases the number. |
| Enabled | Pipeline's Enabled status. If enabled, field is set to True. |
| Created | Date and time this Pipeline was created. |
| Updated | Date and time this Pipeline was last updated. |
Enabling and Disabling Pipelines
Pipelines can be Enabled or Disabled to control their active status and ability to participate in file transfers. The status is defaulted to Enabled and can be changed after creation. The Configuration Item's Disabled status does not impact whether it can be configured. Also, Disabled Endpoints can be added to a Pipeline.
- Enabled (default): The Pipeline is active and allows file transfers.
- Disabled: The Pipeline is inactive and does not allow file transfers.
To enable or disable a Pipeline, follow these steps:
- From the Sidebar, select Configuration > Pipelines.
- Click the Name of the Pipeline you want to enable or disable.
- Click the Enable or Disable button above the Pipeline details.
- If the Pipeline is Disabled, then the button displays Enabled. If the Pipeline is Enabled, then the button displays Disabled.
- Click Update.
Deleting a Pipeline
To delete a UDMG as FTP(S) Client (Pull Scenario) Pipeline, follow these steps:
- From the Sidebar, select Configuration > Pipelines.
- Click the Name of the Pipeline you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button above the Pipeline details.
- You will be asked to confirm the deletion. Click Delete.
Monitoring a Pipeline
To monitor and determine the status of a Pipeline, the Transfers page and Endpoints page must be monitored to track incoming Transfers and the Source and Destination Endpoints' individual statuses, respectively.
On the Transfers page, the following fields indicate the type of Remote Transfer.
- Is Schedule: If Yes, then the Transfer was a Remote Transfer.
- Is Send: If No, then the Remote Transfer was a pull scenario.